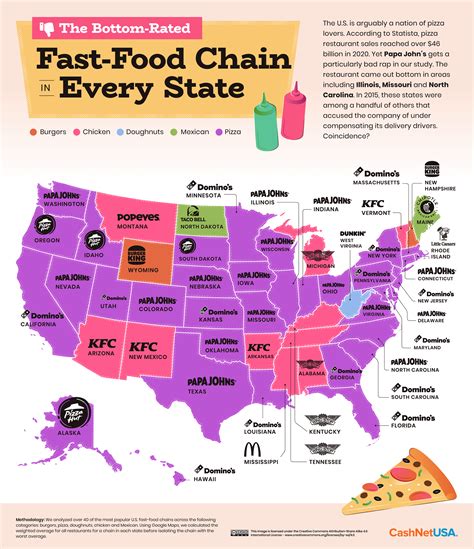
West Virginia claims the title of the state with the highest fast-food consumption in the United States, according to a recent analysis by the consumer review website QSR. The study, analyzing fast-food visits per capita, underscores a notable preference for quick-service dining options among West Virginians.
West Virginia’s fast-food proclivity stands out significantly when compared to national averages. The study indicated that residents of West Virginia visit fast-food restaurants more frequently than individuals in any other state. This high consumption rate points to various underlying factors, including socioeconomic conditions, cultural preferences, and accessibility to fast-food establishments.
QSR’s analysis provides a detailed state-by-state ranking, revealing the states with the highest and lowest fast-food consumption. While West Virginia leads the list, other states with high fast-food consumption include several in the South and Midwest regions. Conversely, states with lower fast-food consumption tend to be concentrated in the Northeast and West Coast.
The reasons behind West Virginia’s high fast-food consumption are multifaceted. Limited access to healthier food options, economic factors, and lifestyle preferences may all contribute to the state’s reliance on fast food. The prevalence of fast-food restaurants in both urban and rural areas of West Virginia further facilitates easy access to these dining options.
QSR’s findings also highlight broader trends in the fast-food industry. Despite growing awareness of health and nutrition, fast food remains a popular choice for many Americans, particularly those seeking convenient and affordable meal options. The fast-food industry continues to adapt to changing consumer preferences by introducing healthier menu items and catering to specific dietary needs.
Diving Deeper into West Virginia’s Fast-Food Consumption
The revelation that West Virginia leads the nation in fast-food consumption raises important questions about the state’s economic, social, and health landscape. A comprehensive examination of the factors contributing to this trend is essential for understanding the full scope of its implications.
Socioeconomic Factors
One of the primary drivers behind West Virginia’s fast-food consumption is its socioeconomic environment. West Virginia has historically faced economic challenges, with higher rates of poverty and unemployment compared to national averages. As noted by economic analysts, “Lower-income populations often rely on fast food as a more affordable and accessible option compared to healthier, but often more expensive, alternatives.” The economic realities of many West Virginians make fast food a practical choice for daily meals.
The U.S. Census Bureau data corroborates this, revealing that West Virginia’s median household income is significantly lower than the national average. This economic disparity directly impacts food choices, pushing many residents towards more budget-friendly options like fast food. Additionally, food insecurity, characterized by limited access to adequate food, is more prevalent in West Virginia than in many other states.
Accessibility and Availability
Another significant factor is the widespread availability of fast-food restaurants throughout West Virginia. Fast-food chains have strategically positioned their outlets in both urban centers and rural communities, ensuring easy access for residents regardless of their location. In many rural areas, fast-food restaurants may be among the few dining options available, making them a default choice for meals.
According to the West Virginia Department of Health and Human Resources, rural areas often lack full-service grocery stores and farmers’ markets that offer fresh produce and healthy food choices. This limited access to nutritious food creates a reliance on fast food, particularly for individuals with transportation challenges or time constraints. The density of fast-food restaurants per capita in West Virginia is notably higher than in states with lower fast-food consumption rates.
Cultural and Lifestyle Factors
Cultural norms and lifestyle preferences also play a role in West Virginia’s fast-food habits. In many communities, fast food has become ingrained in social gatherings and everyday routines. The convenience and speed of fast food cater to busy lifestyles, making it an attractive option for families and individuals seeking quick meal solutions.
“Fast food is often seen as a convenient way to grab a quick meal, especially for those working long hours or juggling multiple responsibilities,” explains Dr. Emily Carter, a sociologist specializing in food culture. “The ease of drive-through services and the familiarity of menu items contribute to its popularity.”
Moreover, regional preferences and tastes can influence food choices. The prevalence of certain fast-food chains in West Virginia and their adaptation to local tastes may further contribute to the state’s high consumption rates. Marketing strategies that target local communities and promote value meals can also drive demand for fast food.
Health Implications
The high consumption of fast food in West Virginia has significant implications for public health. Fast food is often high in calories, saturated fats, sodium, and processed ingredients, contributing to various health problems such as obesity, heart disease, diabetes, and other chronic conditions.
The West Virginia Department of Health and Human Resources has reported alarming rates of obesity and related health issues within the state. “The high prevalence of fast food consumption is undoubtedly a contributing factor to the state’s health challenges,” states Dr. Michael Johnson, a public health official. “Addressing this issue requires a multifaceted approach that includes promoting healthier food options, increasing access to fresh produce, and educating the public about the risks associated with excessive fast-food consumption.”
Studies have shown a direct correlation between frequent fast-food consumption and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The high sugar and fat content in many fast-food items can lead to insulin resistance and weight gain, both of which are major risk factors for diabetes. Similarly, the high sodium content in fast food can contribute to high blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Addressing the Issue
Addressing West Virginia’s high fast-food consumption requires a comprehensive and collaborative effort involving government agencies, healthcare providers, community organizations, and the food industry. Strategies to promote healthier eating habits and improve access to nutritious food are essential for mitigating the negative health impacts associated with fast food.
Policy Interventions
Policy interventions can play a crucial role in shaping food environments and promoting healthier choices. Some potential policy measures include:
- Incentivizing healthy food retailers: Offering tax breaks or subsidies to grocery stores, farmers’ markets, and other businesses that provide fresh produce and healthy food options in underserved areas.
- Implementing zoning regulations: Limiting the density of fast-food restaurants in areas with high rates of obesity and related health problems.
- Increasing funding for nutrition education programs: Providing education and resources to help individuals make informed food choices and adopt healthier eating habits.
- Supporting school-based nutrition initiatives: Implementing healthy school lunch programs and promoting nutrition education in schools.
Community-Based Initiatives
Community-based initiatives can also contribute to improving food access and promoting healthier eating habits. Some examples of such initiatives include:
- Establishing community gardens: Creating community gardens where residents can grow their own fruits and vegetables.
- Supporting local farmers: Promoting local farmers’ markets and encouraging residents to purchase locally grown produce.
- Implementing mobile food markets: Bringing fresh produce and healthy food options to underserved communities through mobile food markets.
- Organizing cooking classes and nutrition workshops: Providing residents with the skills and knowledge they need to prepare healthy meals at home.
Industry Engagement
Engaging the fast-food industry in efforts to promote healthier eating is also essential. Fast-food chains can play a role by:
- Offering healthier menu options: Introducing more nutritious menu items that are lower in calories, fat, sodium, and sugar.
- Reducing portion sizes: Offering smaller portion sizes to help customers control their calorie intake.
- Providing nutrition information: Making nutrition information readily available to customers so they can make informed food choices.
- Marketing healthier options: Promoting healthier menu items through marketing campaigns and in-store promotions.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns can help raise awareness about the health risks associated with excessive fast-food consumption and promote healthier eating habits. These campaigns can use various channels, such as television, radio, social media, and print media, to reach a wide audience.
The messages should focus on:
- The health risks associated with frequent fast-food consumption.
- The benefits of eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Tips for making healthier choices when eating out.
- Resources available to help individuals adopt healthier eating habits.
Long-Term Strategies
Addressing West Virginia’s high fast-food consumption is a long-term endeavor that requires sustained commitment and collaboration. By implementing a multifaceted approach that includes policy interventions, community-based initiatives, industry engagement, and public awareness campaigns, the state can work towards creating a healthier food environment and improving the health outcomes of its residents.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Why does West Virginia consume more fast food than any other state?
Several factors contribute to West Virginia’s high fast-food consumption, including socioeconomic conditions, accessibility to fast-food restaurants, cultural preferences, and limited access to healthier food options. The state’s higher poverty rates and food insecurity mean that fast food is often a more affordable and accessible option for many residents. Additionally, the prevalence of fast-food chains in both urban and rural areas makes it easy for people to access these dining options.
2. What are the health implications of West Virginia’s fast-food consumption?
The high consumption of fast food in West Virginia has significant health implications, contributing to higher rates of obesity, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and other chronic conditions. Fast food is often high in calories, saturated fats, sodium, and processed ingredients, all of which can negatively impact health over time.
3. What is being done to address the high fast-food consumption in West Virginia?
Efforts to address the issue include policy interventions, community-based initiatives, industry engagement, and public awareness campaigns. Policy interventions might include incentivizing healthy food retailers and implementing zoning regulations to limit fast-food restaurant density. Community-based initiatives can focus on establishing community gardens and supporting local farmers. Engaging the fast-food industry to offer healthier menu options and providing nutrition information is also crucial. Public awareness campaigns aim to educate people about the health risks associated with excessive fast-food consumption and promote healthier eating habits.
4. How does West Virginia’s socioeconomic status affect its fast-food consumption?
West Virginia’s lower median household income and higher poverty rates compared to the national average mean that many residents rely on fast food as a more affordable and convenient meal option. The economic realities of many West Virginians make it challenging to afford healthier, but often more expensive, food alternatives. Additionally, food insecurity is more prevalent in West Virginia, further driving the reliance on fast food.
5. What can individuals do to reduce their fast-food consumption in West Virginia?
Individuals can take several steps to reduce their fast-food consumption, including planning meals in advance, cooking at home more often, seeking out healthier fast-food options (such as salads or grilled chicken), and limiting the frequency of fast-food visits. They can also support local farmers’ markets and community gardens to access fresh, affordable produce. Education about nutrition and the health risks of fast food can also empower individuals to make more informed food choices.
Expanded Context and Analysis
The issue of fast-food consumption in West Virginia is not merely a statistic but a reflection of broader societal challenges. Understanding the historical context, economic disparities, and systemic issues that contribute to this trend is crucial for developing effective solutions.
Historical Context
West Virginia’s economic history is closely tied to industries such as coal mining and manufacturing, which have experienced significant decline in recent decades. This decline has led to job losses, economic instability, and a lack of diverse economic opportunities. As a result, many communities have struggled to maintain a strong economic base, leading to higher rates of poverty and food insecurity.
The historical reliance on these industries has also shaped the state’s cultural landscape. Traditional diets in many West Virginian communities have often included high-calorie, processed foods, reflecting the economic realities and lifestyle patterns of the past. This cultural context can influence food preferences and contribute to the continued popularity of fast food.
Economic Disparities
The economic disparities within West Virginia are significant and contribute to variations in fast-food consumption across different regions. Areas with higher poverty rates and unemployment tend to have a greater reliance on fast food, while more affluent communities may have access to a wider range of healthier food options.
The lack of economic opportunities in many rural areas further exacerbates these disparities. Without access to well-paying jobs and stable incomes, residents may find it difficult to afford healthier, more nutritious foods. This economic pressure can lead to a cycle of unhealthy eating habits and poor health outcomes.
Systemic Issues
Several systemic issues contribute to the high fast-food consumption in West Virginia. These include:
- Limited access to healthcare: Many West Virginians lack access to affordable healthcare, making it difficult to address health problems related to poor diet and nutrition.
- Lack of transportation: Limited access to transportation can make it challenging for residents, particularly those in rural areas, to access grocery stores and farmers’ markets that offer fresh produce and healthy food options.
- Insufficient investment in public health: Inadequate funding for public health programs can hinder efforts to promote healthier eating habits and address the underlying causes of poor nutrition.
- Food deserts: Many communities in West Virginia are considered food deserts, meaning they lack access to affordable and nutritious food. This lack of access can lead to a reliance on fast food and other unhealthy options.
The Role of Government and Policy
Government policies can play a significant role in addressing the issue of fast-food consumption in West Virginia. Policies that promote economic development, improve access to healthcare, and support healthy food systems can all contribute to creating a healthier food environment.
Specific policy recommendations include:
- Investing in economic diversification: Supporting new industries and creating job opportunities in sectors beyond coal mining and manufacturing.
- Expanding access to healthcare: Implementing policies that ensure all West Virginians have access to affordable healthcare, including preventive care and nutrition counseling.
- Supporting local food systems: Investing in local farmers, farmers’ markets, and community gardens to increase access to fresh produce and healthy food options.
- Implementing food labeling regulations: Requiring restaurants and food retailers to provide clear and accurate nutrition information to consumers.
- Taxing unhealthy foods: Implementing taxes on sugary drinks and other unhealthy foods to discourage consumption.
- Subsidizing healthy foods: Providing subsidies for fruits, vegetables, and other healthy foods to make them more affordable.
Community-Led Solutions
In addition to government policies, community-led solutions are essential for addressing the issue of fast-food consumption in West Virginia. These solutions can be tailored to the specific needs and challenges of individual communities and can empower residents to take control of their health and well-being.
Examples of community-led solutions include:
- Community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs: Connecting local farmers directly with consumers, providing access to fresh, seasonal produce.
- Mobile food pantries: Delivering food to underserved communities, ensuring that residents have access to nutritious meals.
- Cooking classes and nutrition workshops: Teaching residents how to prepare healthy meals using affordable ingredients.
- Community gardens: Creating spaces where residents can grow their own fruits and vegetables, promoting healthy eating and community engagement.
- Peer support groups: Providing a supportive environment for individuals to share their experiences and learn from each other about healthy eating habits.
The Importance of Education and Awareness
Education and awareness are crucial for changing attitudes and behaviors related to fast-food consumption. By providing individuals with the knowledge and skills they need to make informed food choices, they can take steps to improve their health and well-being.
Educational initiatives can focus on:
- The health risks associated with frequent fast-food consumption.
- The benefits of eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Tips for making healthier choices when eating out.
- Resources available to help individuals adopt healthier eating habits.
- Promoting cooking skills and nutrition literacy.
Conclusion
West Virginia’s high fast-food consumption is a complex issue with deep roots in the state’s economic history, cultural norms, and systemic challenges. Addressing this issue requires a multifaceted approach that includes policy interventions, community-led solutions, and a strong emphasis on education and awareness. By working together, government agencies, healthcare providers, community organizations, and residents can create a healthier food environment and improve the health outcomes of all West Virginians. The challenge is significant, but with sustained commitment and collaboration, West Virginia can transform its food landscape and build a healthier future for its citizens. The data serves as a call to action for comprehensive, community-driven strategies to prioritize nutritional well-being and address the underlying factors driving these trends. Only through a concerted effort can West Virginia shift away from its reliance on fast food and towards a healthier, more sustainable food culture.









