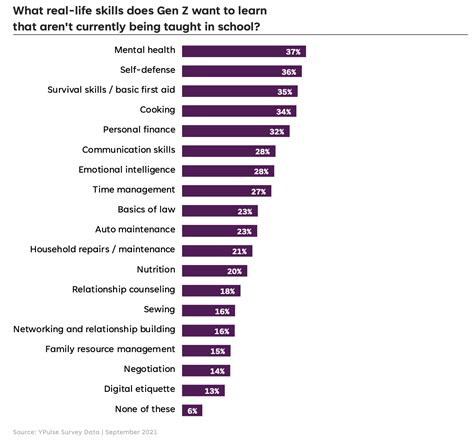
Millennials are voicing concerns about significant gaps in their education, highlighting crucial life skills they feel were inadequately addressed during their schooling, ranging from financial literacy to practical home maintenance.
A recent wave of online discussions reveals that many millennials believe their formal education failed to equip them with essential skills needed for navigating adulthood. Topics such as personal finance, basic home repair, and effective communication consistently emerge as areas where they feel underprepared. The discussions, largely taking place on social media platforms, underscore a growing sentiment that traditional curricula need to evolve to better address the practical needs of today’s young adults.
“I wish they’d taught me how to do my taxes,” shared one user on a popular social media platform, encapsulating a common feeling among millennials. The sentiment is echoed across numerous online forums where young adults lament the lack of instruction in areas vital for independent living. This collective reflection prompts a reevaluation of educational priorities and a push for curricula that encompass a more holistic approach to preparing students for life beyond the classroom.
Financial Literacy: A Recurring Theme
Perhaps the most frequently cited gap is in the realm of financial literacy. Millennials express frustration over the lack of formal instruction in budgeting, investing, understanding credit scores, and managing debt. Many feel they were thrust into the complexities of personal finance without the necessary tools or knowledge to make informed decisions.
“I still don’t fully understand how to invest, and I’m almost 35,” confessed another online participant, highlighting the long-term repercussions of this educational deficit. The consequences can range from poor credit management and mounting debt to a lack of retirement savings and an overall sense of financial insecurity.
The need for financial literacy extends beyond basic budgeting. Millennials express a desire for education on topics such as understanding different types of investments (stocks, bonds, mutual funds), navigating the complexities of the housing market, and planning for long-term financial goals. Without this knowledge, they feel vulnerable to making costly mistakes and struggling to achieve financial stability.
“It’s not just about balancing a checkbook anymore,” says Sarah Miller, a financial advisor specializing in millennial clients. “It’s about understanding the entire financial landscape and making informed decisions that will impact their future.”
Practical Life Skills: Beyond the Classroom
The desire for a more practical education extends beyond finances. Millennials also voice a need for instruction in basic home repair, car maintenance, and other essential life skills. Many feel ill-equipped to handle common household tasks, such as fixing a leaky faucet, changing a tire, or understanding basic electrical wiring.
“I had to watch YouTube videos to learn how to unclog my toilet,” shared one individual, illustrating the reliance on self-taught methods to acquire these skills. While online resources can be helpful, they often lack the hands-on experience and personalized guidance that a formal education could provide.
The absence of these practical skills can lead to increased reliance on outside services, resulting in higher expenses and a sense of helplessness. Moreover, the ability to perform basic repairs and maintenance can empower individuals to be more self-sufficient and resourceful.
“These skills aren’t just about saving money,” explains Mark Johnson, a vocational education instructor. “They’re about building confidence and independence. Knowing how to fix things around the house can be incredibly empowering.”
Communication and Interpersonal Skills: Navigating Relationships
Another area of concern is the lack of emphasis on communication and interpersonal skills. Millennials express a need for education in areas such as conflict resolution, effective communication strategies, and building healthy relationships.
“I wish they’d taught us how to have difficult conversations,” admitted one user. “So many problems could be avoided if we knew how to communicate effectively.”
The ability to communicate clearly and respectfully is essential for navigating personal and professional relationships. Millennials feel that a lack of training in this area has contributed to difficulties in resolving conflicts, building strong teams, and maintaining healthy relationships.
“Communication is the foundation of any successful relationship,” says Dr. Emily Carter, a relationship therapist. “Learning how to express your needs and listen to others is crucial for building trust and resolving conflicts.”
The Role of Education: A Broader Perspective
These concerns raise fundamental questions about the role of education in preparing students for adulthood. Should schools focus solely on academic subjects, or should they also address the practical and interpersonal skills needed for navigating life beyond the classroom?
Many argue that a more holistic approach to education is necessary to ensure that students are well-rounded and equipped to succeed in all aspects of their lives. This includes incorporating financial literacy, practical life skills, and communication skills into the curriculum.
“Education should be about more than just memorizing facts,” argues Dr. David Lee, an education policy expert. “It should be about preparing students to be successful and contributing members of society.”
Potential Solutions: Addressing the Gaps
Several potential solutions have been proposed to address these educational gaps. One approach is to integrate financial literacy and practical life skills into existing curricula. This could involve incorporating lessons on budgeting, investing, and home repair into math, science, and social studies classes.
Another approach is to offer elective courses specifically focused on these topics. These courses could provide students with in-depth instruction and hands-on experience in areas such as personal finance, home maintenance, and communication skills.
Additionally, some schools are exploring partnerships with community organizations and local businesses to provide students with real-world learning opportunities. This could involve internships, apprenticeships, and volunteer experiences that allow students to apply their knowledge and skills in practical settings.
“It’s about creating a more relevant and engaging learning experience for students,” says Lisa Green, a high school principal. “We need to prepare them for the challenges and opportunities they will face in the real world.”
The Impact of Technology: A Double-Edged Sword
While technology has undoubtedly transformed education, it has also contributed to some of the gaps that millennials are experiencing. The focus on digital skills and online learning has sometimes come at the expense of traditional life skills.
Moreover, the constant connectivity and reliance on technology can hinder the development of interpersonal skills. Millennials may struggle to communicate effectively in person or build strong relationships due to their reliance on digital communication.
“Technology is a powerful tool, but it’s not a substitute for real-world skills,” warns Dr. Robert Brown, a technology and education researcher. “We need to find a balance between using technology to enhance learning and ensuring that students develop the essential life skills they need to succeed.”
Looking Ahead: A Call for Change
The concerns voiced by millennials represent a call for change in the education system. There is a growing recognition that schools need to do more to prepare students for the challenges and opportunities of adulthood.
By incorporating financial literacy, practical life skills, and communication skills into the curriculum, schools can empower students to be more self-sufficient, resourceful, and successful in all aspects of their lives. This requires a collaborative effort involving educators, policymakers, parents, and the community as a whole.
“It’s time to rethink what it means to be educated,” concludes Dr. Lee. “We need to prepare students not just for college and careers, but for life itself.”
The ongoing discussions and reflections among millennials underscore the importance of continuously evaluating and adapting educational priorities to meet the evolving needs of society. By addressing these educational gaps, we can better equip future generations with the tools and knowledge they need to thrive in an increasingly complex world.
The COVID-19 Pandemic’s Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic further exacerbated some of these existing educational gaps. With schools shifting to remote learning, many students missed out on hands-on learning experiences and opportunities for social interaction.
The pandemic also highlighted the importance of adaptability and resilience, skills that were not always explicitly taught in schools. Millennials who were already struggling with financial insecurity or mental health challenges faced even greater difficulties during the pandemic.
“The pandemic exposed the vulnerabilities in our education system,” says Dr. Brown. “It reinforced the need for a more holistic approach to education that addresses the social, emotional, and practical needs of students.”
Addressing Generational Differences
It’s important to acknowledge that different generations may have different perspectives on what constitutes essential life skills. What was considered important in the past may not be as relevant today, and vice versa.
However, the fundamental need for financial literacy, practical life skills, and communication skills remains constant. These are essential for navigating adulthood and achieving success in any generation.
“We need to listen to the concerns of millennials and other young adults,” says Green. “They are the ones who are facing the challenges of today’s world, and their insights can help us improve our education system.”
The Role of Parents and Families
While schools play a crucial role in preparing students for adulthood, parents and families also have a significant responsibility. They can supplement the education that students receive in school by providing them with opportunities to learn about financial literacy, practical life skills, and communication skills at home.
This could involve involving children in household tasks, discussing financial matters openly, and modeling effective communication skills. Parents can also encourage their children to pursue extracurricular activities and volunteer opportunities that will help them develop valuable life skills.
“Education is a shared responsibility,” says Miller. “Schools and families need to work together to ensure that students are well-rounded and prepared for the challenges of adulthood.”
Moving Forward: A Collaborative Approach
Addressing the educational gaps identified by millennials requires a collaborative approach involving educators, policymakers, parents, and the community as a whole. This includes:
- Re-evaluating curricula: Incorporating financial literacy, practical life skills, and communication skills into existing curricula.
- Offering elective courses: Providing students with in-depth instruction and hands-on experience in these areas.
- Partnering with community organizations: Providing students with real-world learning opportunities.
- Supporting parents and families: Providing resources and support to help them educate their children about these topics at home.
- Promoting adaptability and resilience: Helping students develop the skills they need to navigate challenges and adapt to change.
- Embracing technology thoughtfully: Using technology to enhance learning while ensuring that students develop essential life skills.
- Listening to the voices of young adults: Incorporating their insights and perspectives into the education system.
By working together, we can create a more relevant and engaging education system that prepares students for the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century.
Long-Term Benefits of Addressing Educational Gaps
Addressing these educational gaps is not just about improving individual outcomes; it’s about strengthening society as a whole. By equipping young adults with the skills they need to succeed, we can:
- Reduce poverty and inequality: Financial literacy and practical life skills can help individuals break the cycle of poverty and achieve financial stability.
- Strengthen the economy: A well-educated and skilled workforce is essential for economic growth and competitiveness.
- Improve public health: Financial literacy and communication skills can help individuals make informed decisions about their health and well-being.
- Promote civic engagement: A more informed and engaged citizenry is essential for a healthy democracy.
- Create a more just and equitable society: By addressing the educational gaps that disproportionately affect marginalized communities, we can create a more just and equitable society for all.
The challenges highlighted by millennials serve as a catalyst for positive change in education. By acknowledging these gaps and working collaboratively to address them, we can empower future generations to thrive and contribute to a more prosperous and equitable world. It’s an investment not just in individual success, but in the overall well-being of society.
Further Considerations and Research
The ongoing discussion surrounding millennial perspectives on educational gaps also highlights several areas that warrant further consideration and research:
- The impact of student loan debt: Many millennials are burdened by significant student loan debt, which can hinder their ability to save for retirement, purchase a home, or start a family. Research is needed to understand the long-term impact of student loan debt on millennial financial well-being and to explore potential solutions, such as debt forgiveness or income-driven repayment plans.
- The changing nature of work: The job market is constantly evolving, and many traditional career paths are becoming obsolete. Research is needed to understand the skills and knowledge that will be most in-demand in the future and to ensure that students are prepared for the jobs of tomorrow. This may involve focusing on skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, creativity, and adaptability.
- The importance of mental health: Mental health challenges are increasingly prevalent among young adults. Research is needed to understand the factors that contribute to mental health problems and to develop effective interventions to promote mental well-being. This may involve incorporating mental health education into the curriculum and providing students with access to counseling and support services.
- The role of technology in education: Technology has the potential to transform education, but it also poses challenges. Research is needed to understand how to use technology effectively to enhance learning and to address the potential negative consequences of technology, such as social isolation and cyberbullying.
By conducting further research in these areas, we can gain a deeper understanding of the challenges facing young adults and develop more effective strategies to support their success.
Conclusion: A Generational Imperative
The millennial generation’s reflection on their educational experiences serves as a powerful reminder of the need for continuous improvement and adaptation in our education system. Their voices highlight the critical importance of equipping students not only with academic knowledge but also with the practical life skills, financial literacy, and interpersonal abilities necessary to navigate the complexities of adulthood and contribute meaningfully to society. By embracing a collaborative approach and prioritizing these essential skills, we can empower future generations to thrive and create a more prosperous and equitable world for all. The imperative to address these educational gaps is not just a matter of generational equity, but a fundamental investment in the future of our communities and the well-being of society as a whole. The ongoing dialogue and commitment to action will shape a more relevant, responsive, and ultimately more effective education system for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What specific life skills do millennials feel they missed out on in school?
Millennials frequently cite a lack of education in financial literacy (budgeting, investing, taxes), practical life skills (home repair, car maintenance), and communication/interpersonal skills (conflict resolution, effective communication). Many express feeling unprepared for the realities of managing personal finances and household responsibilities after leaving school.
2. Why is financial literacy considered such a significant gap in millennial education?
Financial literacy is crucial for making informed decisions about managing money, debt, and investments. Millennials often enter adulthood without a solid understanding of these concepts, leading to potential financial instability, poor credit management, and difficulties in achieving long-term financial goals like homeownership or retirement savings. The complexities of modern finance require a foundational understanding that many feel was lacking in their education.
3. How did the COVID-19 pandemic exacerbate these educational gaps?
The pandemic disrupted traditional learning environments, shifting education online and limiting hands-on learning opportunities. This further reduced the chances for students to develop practical skills and interpersonal abilities. The pandemic also highlighted the need for adaptability and resilience, skills that were not always explicitly taught in schools and became essential for navigating the challenges of the crisis.
4. What are some proposed solutions to address these educational shortcomings?
Proposed solutions include integrating financial literacy and practical life skills into existing curricula (e.g., incorporating budgeting into math classes), offering elective courses specifically focused on these topics, partnering with community organizations for real-world learning experiences, and providing resources and support to parents and families to reinforce these skills at home.
5. What is the long-term impact of addressing these educational gaps?
Addressing these gaps can have a positive impact on individual well-being, economic stability, and societal progress. Equipping young adults with essential life skills can reduce poverty and inequality, strengthen the economy, improve public health, promote civic engagement, and create a more just and equitable society overall. It is an investment in both individual success and the overall well-being of communities.









