U.S. airlines are projected to collect a staggering $7.2 billion in baggage fees this year, underscoring the increasing reliance on ancillary revenue streams within the aviation industry, according to recent data. This record-breaking figure highlights a significant shift in how airlines generate revenue, impacting both their financial performance and consumer travel costs.
Airlines have consistently increased revenue from checked baggage fees over the past decade, transforming what was once a complimentary service into a substantial source of income. The projection, derived from an analysis of financial reports and industry trends, indicates that baggage fees are becoming an ever more critical component of airline profitability. “The revenue generated from baggage fees has become an integral part of airlines’ financial strategy, enabling them to offset operational costs and maintain competitive pricing in base fares,” explains travel industry analyst, John Edwards. This financial strategy allows airlines to offer lower initial ticket prices, attracting a broader range of customers while recouping costs through additional fees.
This revenue bonanza from baggage fees coincides with a broader trend of airlines unbundling services. Where once ticket prices included meals, seat selection, and checked baggage, now many of these are offered as separate add-ons. This allows airlines to present lower base fares, making air travel appear more affordable at first glance. However, travelers who require these additional services often find themselves paying significantly more than they would have under the old bundled system.
The increasing reliance on baggage fees also reflects changes in consumer behavior and travel patterns. With more travelers seeking budget-friendly options, airlines have capitalized on the demand for lower fares by separating services. The growth of low-cost carriers has further fueled this trend, pushing legacy airlines to adopt similar pricing strategies to remain competitive. This has resulted in a landscape where baggage fees are now commonplace across the entire airline industry.
The implications of this trend extend beyond just financial considerations. Travelers are now faced with the added complexity of navigating a maze of fees and restrictions when booking flights. Understanding baggage allowances, weight limits, and additional charges has become essential for avoiding unexpected costs at the airport. This can lead to frustration and a sense of being nickel-and-dimed by airlines.
Moreover, the increased scrutiny on baggage fees has prompted debates about transparency and fairness in airline pricing. Consumer advocacy groups have called for greater disclosure of fees and more standardized baggage policies across different airlines. They argue that airlines should be more upfront about the true cost of travel, including all potential fees, to ensure that consumers can make informed decisions. The lack of transparency can lead to customers not realizing the extra costs they will incur and could choose an airline that doesn’t meet their needs effectively.
The $7.2 billion projection for baggage fees underscores the significant impact of these charges on both airlines and travelers. As the aviation industry continues to evolve, it remains to be seen how airlines will balance the need for revenue generation with the desire to provide a positive customer experience. The challenge will be to find a sustainable model that benefits both airlines and passengers alike, ensuring transparency, fairness, and value for money.
Detailed Analysis
The projection of $7.2 billion in baggage fees represents a substantial increase compared to previous years. Several factors contribute to this growth, including increased passenger numbers, higher baggage fees, and stricter enforcement of weight and size restrictions. Airlines have become more adept at managing baggage operations, leveraging technology and data analytics to optimize pricing and maximize revenue. For example, airlines have implemented dynamic pricing models for baggage fees, adjusting prices based on demand, route, and time of year. This allows them to capture more revenue during peak travel periods and incentivize travelers to purchase baggage allowances in advance.
Furthermore, airlines have invested in infrastructure and technology to streamline baggage handling processes. Automated baggage sorting systems, RFID tracking, and self-service baggage kiosks have improved efficiency and reduced the costs associated with baggage operations. This enables airlines to offer baggage services more profitably, contributing to the overall growth in baggage fee revenue. The technology also leads to fewer lost bags, which is a growing consumer concern.
However, the reliance on baggage fees also poses challenges for airlines. The negative perception of these fees among travelers can impact customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. Passengers often view baggage fees as a hidden cost and feel that they are being exploited by airlines. This can lead to resentment and a willingness to switch to airlines with more transparent pricing policies. The need to balance revenue generation with customer satisfaction is crucial for long-term success.
Airlines are also facing increased competition from alternative modes of transportation, such as trains and buses, particularly on short-haul routes. These modes of transport often offer more generous baggage allowances and fewer restrictions, making them an attractive option for travelers who want to avoid baggage fees. Airlines need to carefully consider the competitive landscape when setting baggage fees to ensure that they remain competitive and do not alienate potential customers. Many customers are more willing to drive than fly short distances to avoid baggage fees, causing airlines to miss out on significant business opportunities.
In addition, the increasing scrutiny of baggage fees by regulatory authorities and consumer advocacy groups could lead to changes in airline pricing practices. Governments in some countries have already imposed regulations on baggage fees, such as requiring airlines to disclose fees upfront or limiting the amount that can be charged. Further regulation could impact airlines’ ability to generate revenue from baggage fees and force them to find alternative sources of income. Some lawmakers are pushing for the regulations in the United States as well.
The trend towards unbundling services and charging for extras is not unique to the airline industry. Other sectors, such as hotels, rental cars, and entertainment, have also adopted similar pricing strategies. However, the airline industry has been particularly aggressive in unbundling services, leading to greater scrutiny and criticism. Passengers see the airline industry as one that is taking advantage of the system.
Consumer Impact
The rise of baggage fees has significantly impacted the way people travel. Travelers are now more likely to pack lighter, ship their luggage in advance, or use alternative modes of transport to avoid these charges. Many passengers try to fit everything into carry-on bags, leading to crowded overhead bins and delays in boarding and deplaning. This can create a stressful and unpleasant travel experience for all passengers.
The increasing complexity of airline pricing also makes it more difficult for travelers to compare prices and find the best deals. The base fare advertised by an airline may not reflect the true cost of travel, as baggage fees, seat selection fees, and other charges can significantly increase the overall price. Consumers need to carefully read the fine print and compare all potential fees before making a booking. Many consumers don’t read the fine print, leading to financial difficulties at the airport when they are asked to pay these fees.
Moreover, the lack of transparency in airline pricing can lead to confusion and frustration. Passengers may not be aware of the baggage allowance or weight limits until they arrive at the airport, at which point they are forced to pay hefty fees for overweight or oversized bags. This can create a negative impression of the airline and damage its reputation.
Consumer advocacy groups are working to promote greater transparency and fairness in airline pricing. They are calling on airlines to disclose all fees upfront and to provide more standardized baggage policies across different airlines. They are also advocating for regulations to protect consumers from unfair or deceptive pricing practices. It’s not unheard of for a customer to pay more in baggage fees than for the ticket itself.
Some airlines have responded to these concerns by offering more transparent pricing and more generous baggage allowances. For example, some airlines offer free checked baggage to passengers who purchase higher-fare tickets or who are members of their loyalty programs. Others have simplified their baggage policies and made it easier for passengers to understand the fees and restrictions. These efforts can improve customer satisfaction and build brand loyalty.
Industry Perspective
From the perspective of airlines, baggage fees are a necessary tool for generating revenue and maintaining profitability. The airline industry is highly competitive, with airlines constantly under pressure to lower fares and attract customers. Baggage fees allow airlines to offer lower base fares while still covering their operating costs. Without baggage fees, airlines would likely have to raise base fares, making air travel less affordable for many people.
Airlines also argue that baggage fees are fair because they charge passengers only for the services they use. Passengers who do not check bags do not have to pay baggage fees, while those who do check bags pay for the cost of handling and transporting their luggage. This allows airlines to offer a more customized service and to cater to the needs of different types of travelers. Some airlines also have fees for premium carry-on space which further allows consumers to customize their experience.
Moreover, airlines argue that baggage fees encourage passengers to pack lighter, reducing the weight of the aircraft and saving fuel. This can lead to lower emissions and a more environmentally friendly travel experience. While this may be true to an extent, the primary motivation for airlines is revenue generation rather than environmental concerns. Some consumer advocates believe this is an excuse for additional revenue for airlines.
The airline industry is constantly evolving, and airlines are always looking for new ways to generate revenue and improve profitability. Baggage fees are just one example of the many ancillary revenue streams that airlines have developed in recent years. Other examples include seat selection fees, priority boarding fees, and in-flight entertainment fees. These ancillary revenue streams are becoming increasingly important for airlines, as they help to offset rising costs and maintain competitive pricing.
Historical Context
Baggage fees were not always a standard practice in the airline industry. For many years, airlines included checked baggage as part of the base fare. However, in the early 2000s, as airlines faced increasing financial pressures due to rising fuel costs and increased competition, they began to unbundle services and charge separately for checked baggage.
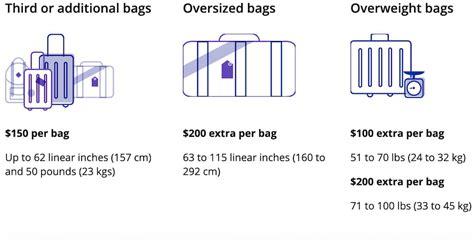
The first major U.S. airline to introduce baggage fees was American Airlines in 2008. Other airlines quickly followed suit, and baggage fees soon became commonplace across the entire industry. Initially, baggage fees were relatively low, typically around $25 for the first checked bag. However, over time, airlines have gradually increased baggage fees, and they now range from $30 to $40 or more for the first checked bag, depending on the airline, route, and fare class.
The introduction of baggage fees was met with criticism from consumers, who viewed them as a hidden cost and a way for airlines to nickel-and-dime passengers. However, airlines argued that baggage fees were necessary to maintain profitability and to keep base fares low. They also pointed out that passengers who did not check bags could avoid the fees altogether.
Over time, consumers have become more accustomed to baggage fees, and they are now widely accepted as a standard part of air travel. However, the level of baggage fees and the lack of transparency in airline pricing remain a source of frustration for many travelers.
Future Trends
The trend of airlines relying on baggage fees is likely to continue in the future. As airlines face increasing cost pressures and competition, they will need to find new ways to generate revenue and maintain profitability. Baggage fees are a relatively easy way to generate revenue, as they are paid by a large percentage of passengers.
However, the future of baggage fees may also be shaped by regulatory changes and consumer advocacy efforts. Governments in some countries may impose regulations on baggage fees, such as requiring airlines to disclose fees upfront or limiting the amount that can be charged. Consumer advocacy groups may also continue to push for greater transparency and fairness in airline pricing.
Airlines may also explore new ways to offer baggage services, such as offering more flexible baggage allowances or providing incentives for passengers to pack lighter. Some airlines are already experimenting with these types of programs. For example, some airlines offer discounts on baggage fees to passengers who purchase baggage allowances in advance or who are members of their loyalty programs.
The challenge for airlines will be to balance the need for revenue generation with the desire to provide a positive customer experience. Airlines that are able to find a sustainable model that benefits both airlines and passengers alike will be the most successful in the long run.
FAQ Section
Q1: How much are U.S. airlines expected to make in baggage fees this year?
A1: U.S. airlines are projected to collect $7.2 billion in baggage fees this year. This figure represents a significant portion of their ancillary revenue.
Q2: Why are baggage fees becoming such a significant revenue source for airlines?
A2: Baggage fees have become a significant revenue source due to several factors, including increased passenger numbers, higher fees, stricter enforcement of weight and size restrictions, and the unbundling of services. This allows airlines to offer lower base fares while recouping costs through additional charges.
Q3: How have baggage fees impacted the way people travel?
A3: Baggage fees have led travelers to pack lighter, ship luggage in advance, or use alternative modes of transportation to avoid charges. This has also resulted in crowded overhead bins on flights.
Q4: What are consumer advocacy groups doing about baggage fees?
A4: Consumer advocacy groups are pushing for greater transparency and fairness in airline pricing. They advocate for airlines to disclose all fees upfront and standardize baggage policies across different airlines, helping consumers make informed decisions.
Q5: Are there any alternatives to paying baggage fees?
A5: Yes, several alternatives exist. These include packing lighter to meet carry-on requirements, shipping luggage in advance via mail services, using alternative modes of transportation like trains or buses, or opting for airlines or credit cards that offer free checked baggage as a perk.